A Buyer’s Guide for EV Charging Cables
Last updated:
If you're new to electric vehicles, choosing the right charging cable can be a bit overwhelming.
You are probably wondering, if you should buy a cable at all and if so, which one is the right one.
In this article we will guide you through this decision-making process and help you get familiar with the EV charging modes and types of plugs. Knowing what they mean will make you feel much more confident when buying a cable.
So, let's get started!
Do you want to allow Integration of youtube videos?
Allows the playback of videos, that are hosted on youtube.com. By allowing this feature, you accept the privacy agreement of google.
Do I Really Need to Buy a Charging Cable?
Short answer: yes, you should.
Why?
If you bought a home charger, whether mobile or stationary, you will need a cable to connect it with your EV. The thing is, most charging stations come without one. Therefore, you will need to buy a cable separately.
When you use public charging stations (e.g. near a supermarket, gym or office building), you often have to use your own cable to charge your car. If you don’t have one, you simply won’t be able to charge.
And honestly, it is always nice to know you have a charging cable in the back of the car in case you find yourself somewhere unexpected. This way you don’t have to worry.
Now, let’s have a look at the EV charging modes and plug types, as this will help you make an informed decision and feel at ease when buying a cable.
EV Charging Modes
There are four main charging modes, each of which requires a different cable. These Modes differ in safety, speed and mobility of charging.
You will see that you can only select charging cables for charging modes 2 and 3.
You do not need to buy a separate cable for modes 1 and 4.
Nevertheless, let's take a look at all four charging modes.
Mode 1 charging
This Mode is represented by a basic cable for AC supply to the car. You simply plug one end into the socket on your wall and the other end into your vehicle.
There is no “box” in between, which means a complete absence of a control system and electrical protection. Electricity just keeps flowing.
Therefore, it's not safe for your house and car and restricted in many countries.
Mode 2 charging
Unlike Mode 1, Mode 2 charging incorporates means of communication with the car and means of protection against electric shocks. This ensures greater safety for both the user and the vehicle. Like with Mode 1, the users can plug/unplug the charger themselves, so it is considered a portable charger.
The go-e Charger Gemini flex is a Mode 2 charger - it's portable and doesn’t require an electrician to install. However, unlike many other Mode 2 chargers, it can also be used as a regular wallbox in the wall bracket.
Mode 3 charging
This is the most common method of charging with AC power.
It functions similarly to the Mode 2 charging, except that the wallbox is hardwired into the car parking/building's electrical supply. Therefore it's not portable. The cable can be attached to the charger or you need to use your own one.
The go-e Charger Gemini is a Mode 3 charger.
Mode 4 charging
Whereas with Mode 1-3 charging, the AC current is converted to DC inside the car, with Mode 4 charging, the AC to DC conversion takes place inside the charging station and not in the car, so the DC current is supplied to the car.
Mode 4 charging is more commonly known as DC charging.
You don’t have to choose a cable for this Mode as it is always attached to the DC charging station.
As mentioned, although we have provided you with an overview of all four Modes, you can actually only select a cable for charging Modes 2 and 3.
Now, let’s have a look at the charging plugs.
Types of Charging Plugs for Electric Cars
In Europe, the one end of the cable, which you are plugging into the charger, will always be type 2. Other places may have a type 1 socket in the charger. The other end of the cable though, the one which is plugged into the EV, can vary depending on the car model and country it is manufactured in.
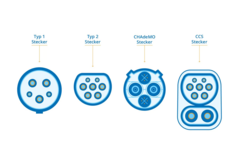
Here are four main EV plug types:
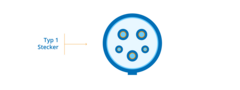
EV Plug Type 1
The type 1 plug is not very common nowadays. It can be used for AC single-phase charging only. Its maximum power output is 7.4 kW.
Suitable e.g. for the following electric vehicles:
Kia Soul EV, Mitsubishi I-MIEV, Mitsubishi Outlander PHEV, Nissan Leaf 2012-2017, Citroen C-Zero, Peugeot iOn, Renault Fluence, etc.
Shape:
The type 1 socket is perfectly round and has 5 pin holes for inserting a plug.
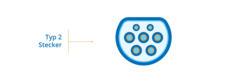
EV Plug Type 2
The type 2 plug is the standard adopted throughout Europe. Only AC charging is possible with it. Unlike type 1 plug, type 2 enables charging with three phases. The maximum power rate of the cable with a type 2 plug is 22 kW for private charging and 43 kW for public charging.
Suitable e.g. for the following electric vehicles:
Audi, BMW, Hyundai, KIA, Mercedes, Nissan Leaf 2018, Range Rover P400e, Renault Zoe, Tesla, Toyota, Volkswagen, etc.
Shape:
The type 2 socket is shaped like a circle with ¾ of the top cut out and has 7 pin holes.
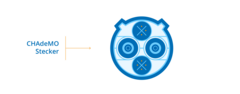
CHAdeMO
CHAdeMO is more commonly used by Asian car manufacturers. It’s important to note that this type of plug can be used for DC charging only. The maximum power output you can get with it is 350 kW. Note, however, that the speed limit varies from one public charging station to another.
Suitable e.g. for the following electric vehicles:
Mitsubishi i-MiEV, Nissan LEAF, Mitsubishi Outlander PHEV, Nissan e-NV200, KIA Soul, etc.
Shape:
The socket consists of four large pin holes. The upper and lower ones are represented by 4 additional small pin holes each.
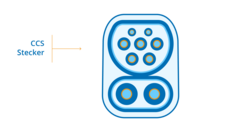
CCS
The CCS (Combined Charging System) is very common, but it can be used for both DC and AC charging. The "2-in-1" plug is also called Combo 2 because of its dual function. The maximum power rate you can reach with this plug when charging with a direct current is 350 kW.
Suitable e.g. for the following electric vehicles:
BMW i4, Peugeot e-2008, Fiat 500e, Hyundai Kona Elektro, Audi Q4 e-tron, Skoda Enyaq iV, etc.
Shape:
The design of the CCS socket for this plug is pretty interesting. It basically looks like a type 2 socket with two additional pin holes below.
Note: Tesla is using a modified form of the Mennekes type 2 plug for its superchargers (available at public charging points only). This enables the Model S to charge up to 80% within 30 minutes.
Here a visual summary of the four different plug types we have just described.
So, we got familiar with the charging modes and the plug types.
Now let’s talk about which cable is the right one for you.
Which Cable is the Right One for Me?
To find out which charging cable is right for you, follow these four steps:
Step 1: Find out what socket your car has
Most probably, your electric vehicle is equipped with either a type 1 or type 2 socket for AC charging. If your EV has a CCS socket it also has a type 2 socket integrated.
Step 2: According to the socket type of your car, choose a suitable plug
The one end of the cable, which you are plugging into the socket in the charger, will always be type 2. The other end of the cable, which goes into the socket of the electric car, can vary.
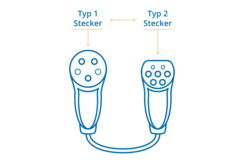
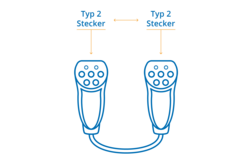
Therefore, you will need either:
-
Type 1 to Type 2 cable: a charging cable with a type 1 plug on one end and a type 2 plug on the other end
-
Type 2 to Type 2 cable: a charging cable with type 2 plugs on both ends
Step 3: Define the current rating of the cable you need
Each EV charging cable comes with a certain charging power limit. It can be 3.6 kW, 7.2 kW or higher.
Selecting one with the highest possible charging speed in mind is a future-oriented decision.
For instance, go-e offers cables that are capable of charging at up to 22 kW. Such a cable will allow you to charge your car at the maximum speed it can be charged (consider the max speed the charging unit is capable of providing).
Step 4: Decide on the perfect length
If you are buying a charging cable purely for home use, it should be as short as possible so that it takes up less space and is easier to handle.
But in reality, most EV drivers always want to have a cable with them to be able to use it at public charging points. And here, it is important to have a long enough charging cable to reach the charging station even in an unfavourable situation. Charging stations are not always ideally located and, therefore, parking near them can be quite a challenge.
But what’s long and what’s short in terms of a charging cable? Well, you can get a cable that is 7.5 metres long or even longer. Such options can be useful if you install the charger really far from the place where you can park your car.
In most cases, however, the cable shouldn’t be longer than 7.5 metres.
For instance, we are offering the following lengths: 2.5 m, 5 m and 7.5 m.
The longer the cable, the heavier it is and the more space it takes up in the boot. Therefore the cable should not be longer than necessary.
go-e type 2 charging cable Black Edition (up to 22 kW) 7.5 m

Practical solution for situations where a car cannot be parked directly next to the charging station. The cable length allows two cars to be charged without having to move one of them.
go-e type 2 charging cable Black Edition (up to 22 kW) 5 m

The go-e cable for a maximum charging power of 22 kW is easy to handle. It is suitable for all electric vehicles with a type 2 plug. It can be used at both stationary and mobile charging stations.
go-e type 2 charging cable Black Edition (up to 22 kW) 2.5 m

You can park your electric car right next to the charging station? Then this cable is the perfect choice for you. It can remain permanently connected to the wallbox or be taken with you on your travels to charge at any wallbox or public charging station.
Adapters for the Charger: Do You Need One?
A charging cable will allow you to charge your car battery wherever you find a charger. If there are no charging points in the area where you travel, a mobile charging station will come handy. Simply plug it into a socket and connect it to your car with a cable. The only thing is that finding a suitable socket might be quite tricky.
Most mobile chargers come with a CEE red plug. If you haven’t got a corresponding socket, keep calm and look for adapters. With them, you can connect your mobile charger to one of the following sockets:
- multiple domestic plugs (household power outlets)
- CEE blue 16 A (camping plug)
- CEE red 16/32 A (three-phase current) - depending on the plug of your charger
We suggest you get an adapter set. An adapter set 11 kW or 22 kW allows you to be ready to go camping, spend some time in your holiday house or charge your car while visiting friends.
Summary
Getting to know the world of EV mobility is easier if you are familiar with the basic terms. Now you are aware of the types of charging plugs and can distinguish between charging Mode 1 and Mode 3. And whenever you want to buy a cable to charge your EV, you can always come back here and check out the cable selection guide once again.